The Data Plane
The data-plane data model is a directed, acyclic [1] graph of heterogeneous objects. A packet will forward walk the graph as it is switched. Each object describes the actions to perform on the packet. Each object type has an associated VLIB graph node. For a packet to forward walk the graph is therefore to move from one VLIB node to the next, with each performing the required actions. This is the heart of the VPP model.
The data-plane graph is composed of generic data-path objects (DPOs). A parent DPO is identified by the tuple:{type,index,next_node}. The next_node parameter is the index of the VLIB node to which the packets should be sent next, this is present to maximise performance - it is important to ensure that the parent does not need to be read [2] whilst processing the child. Specialisations [3] of the DPO perform distinct actions. The most common DPOs and briefly what they represent are:
Load-balance: a choice in an ECMP set.
Adjacency: apply a rewrite and forward through an interface
MPLS-label: impose an MPLS label.
Lookup: perform another lookup in a different table.
The data-plane graph is derived from the control-plane graph by the objects therein 'contributing' a DPO to the data-plane graph. Objects in the data-plane contain only the information needed to switch a packet, they are therefore simpler, and in memory terms smaller, with the aim to fit one DPO on a single cache-line. The derivation from the control plane means that the data-plane graph contains only object whose current state can forward packets. For example, the difference between a fib_path_list_t and a load_balance_t is that the former expresses the control-plane's desired state, the latter the data-plane available state. If some paths in the path-list are unresolved or down, then the load-balance will not include them in the forwarding choice.
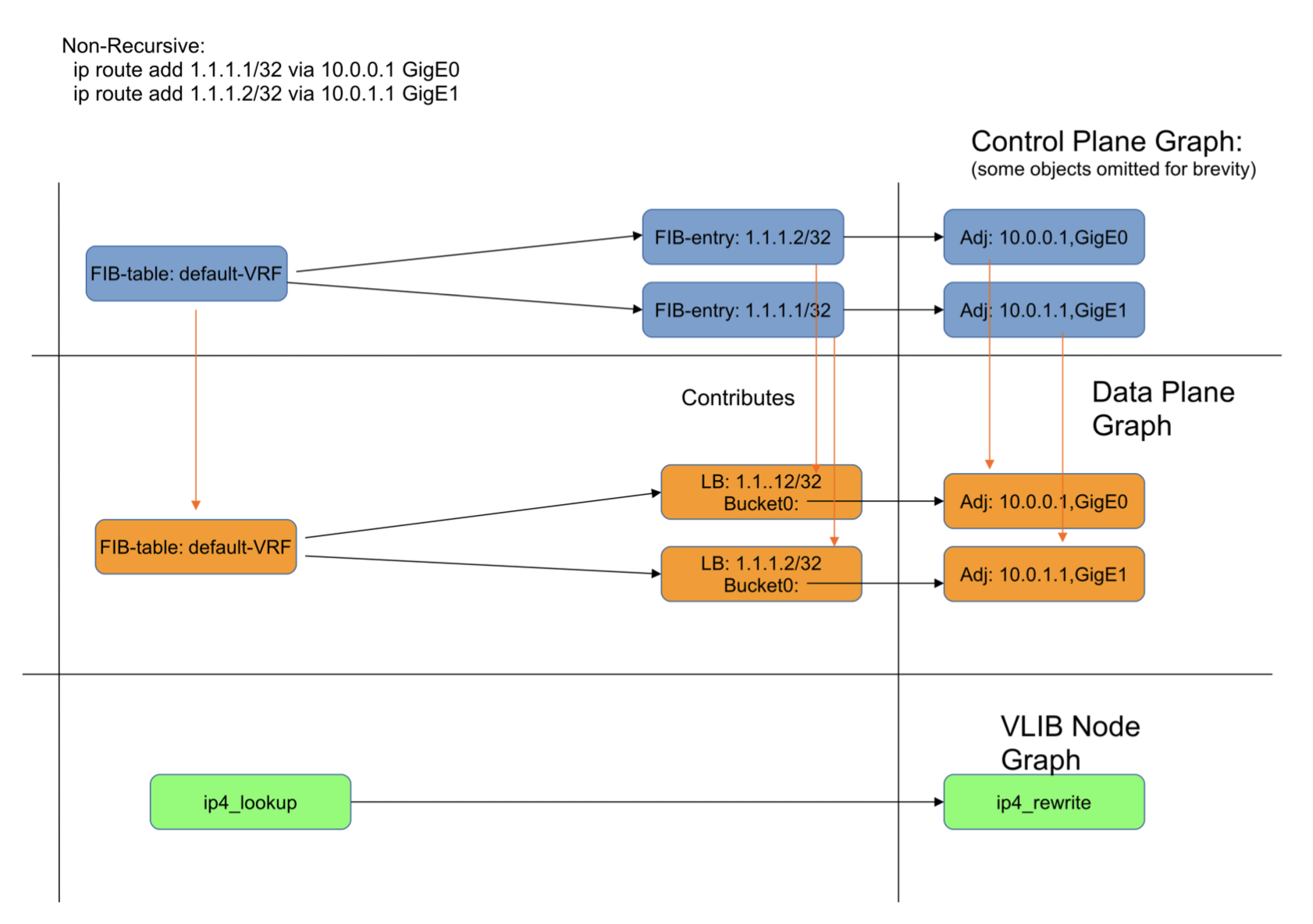
Figure 8: DPO contributions for a non-recursive route
Figure 8 shows a simplified view of the control-plane graph indicating those objects that contribute DPOs. Also shown are the VLIB node graphs at which the DPO is used.
Each fib_entry_t contributes it own load_balance_t, for three reasons;
The result of a lookup in a IPv[46] table is a single 32 bit unsigned integer. This is an index into a memory pool. Consequently the object type must be the same for each result. Some routes will need a load-balance and some will not, but to insert another object in the graph to represent this choice is a waste of cycles, so the load-balance object is always the result. If the route does not have ECMP, then the load-balance has only one choice.
In order to collect per-route counters, the lookup result must in some way uniquely identify the fib_entry_t. A shared load-balance (contributed by the path-list) would not allow this.
In the case the fib_entry_t has MPLS out labels, and hence a fib_path_ext_t, then the load-balance must be per-prefix, since the MPLS labels that are its parents are themselves per-fib_entry_t.
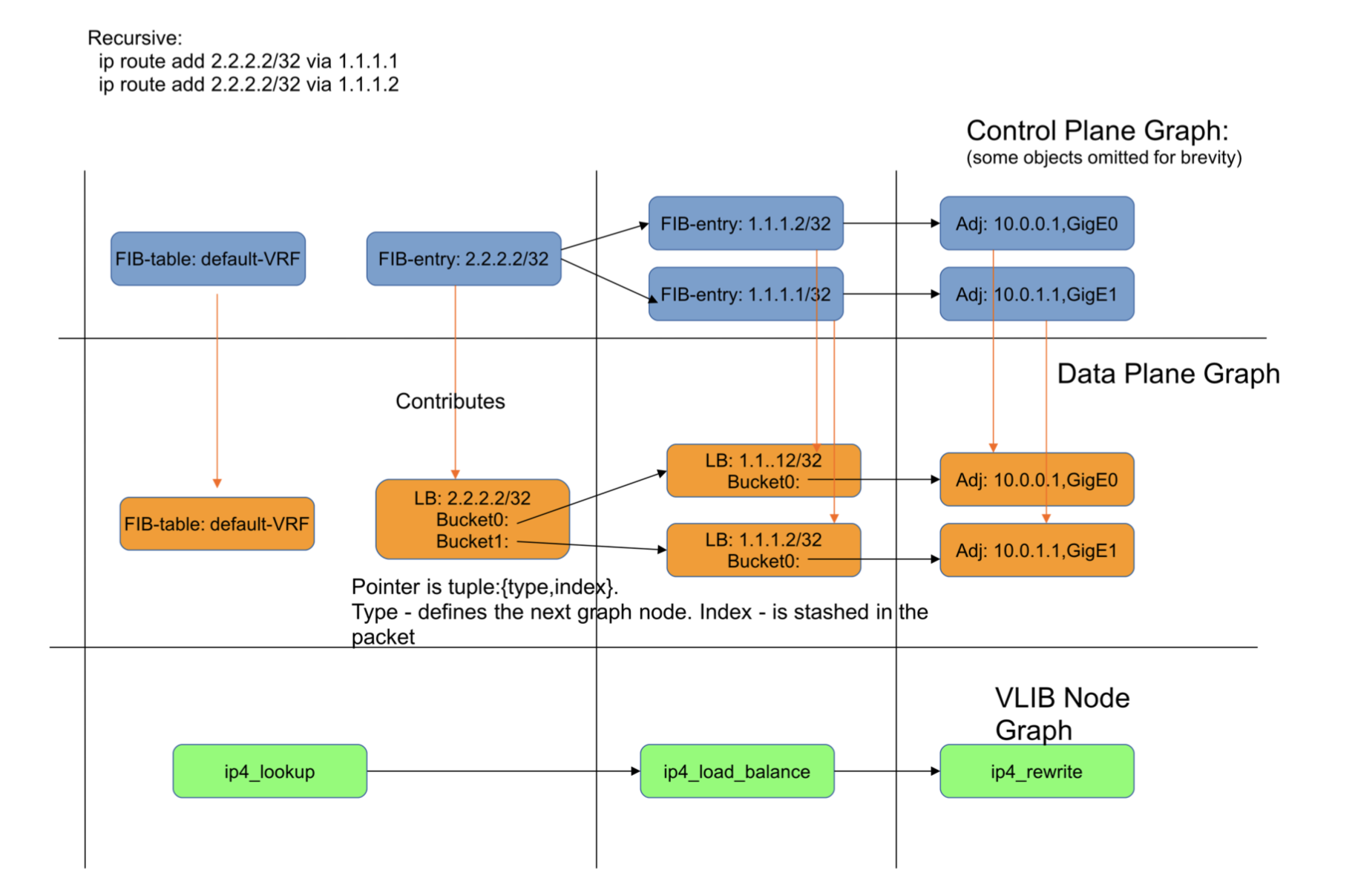
Figure 9: DPO contribution for a recursive route.
Figure 9 shows the load-balance objects contributed for a recursive route.
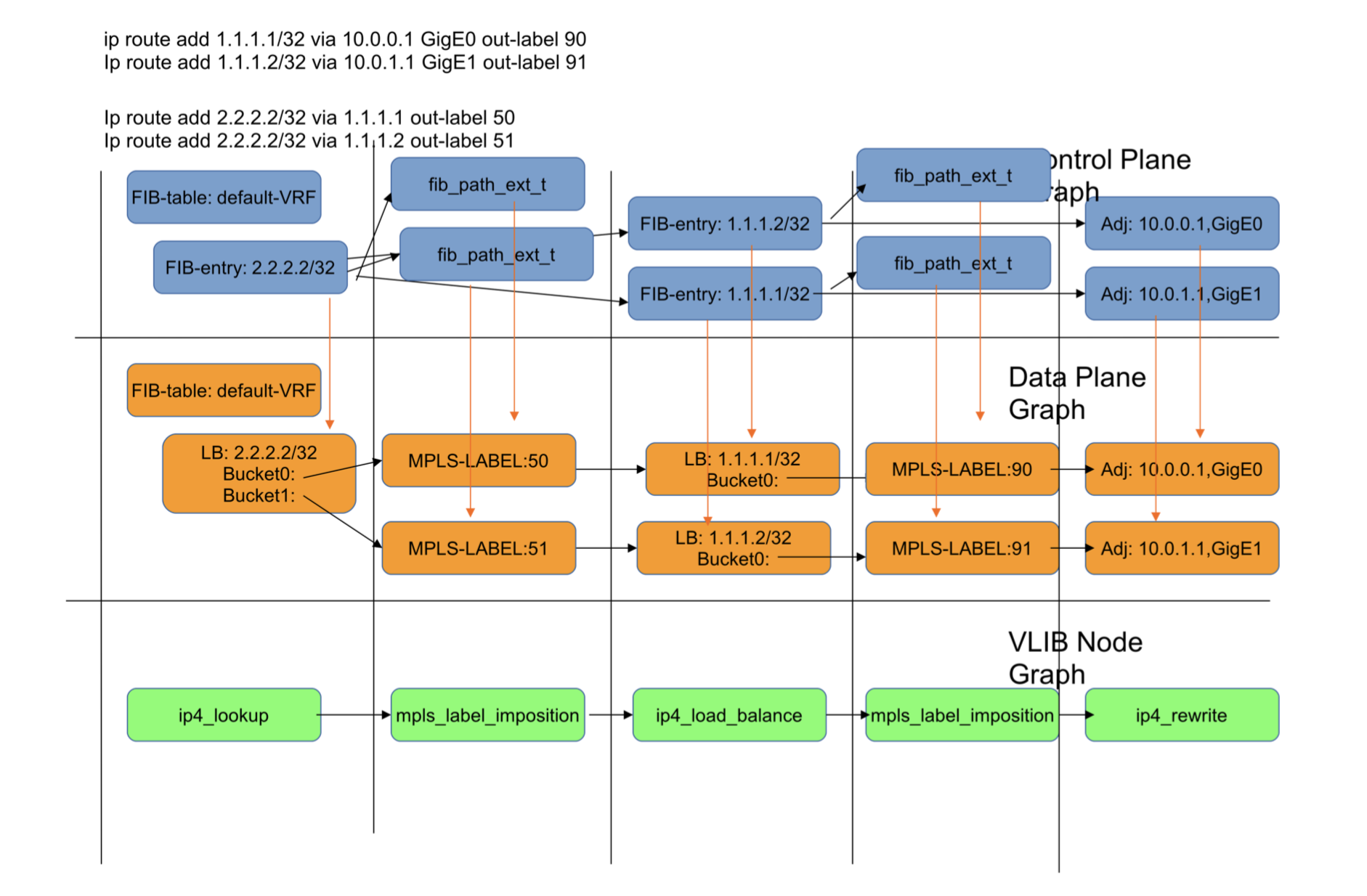
Figure 10: DPO Contributions from labelled recursive routes.
Figure 10 shows the derived data-plane graph for a labelled recursive route. There can be as many MPLS-label DPO instances as there are routes multiplied by the number of paths per-route. For this reason the mpls-label DPO should be as small as possible [4].
The data-plane graph is constructed by 'stacking' one instance of a DPO on another to form the child-parent relationship. When this stacking occurs, the necessary VLIB graph arcs are automatically constructed from the respected DPO type's registered graph nodes.
The diagrams above show that for any given route the full data-plane graph is known before any packet arrives. If that graph is composed of n objects, then the packet will visit n nodes and thus incur a forwarding cost of approximately n times the graph node cost. This could be reduced if the graph were collapsed into fewer DPOs and nodes. There are two ways we might consider doing this:
write custom DPOs/nodes for combined functions, e.g. pop MPLS label and lookup in v4 table. This has the disadvantage that the number of such nodes would be, well, combinatorial, and resolving a path via a combined DPO would be more difficult as it would involve a forward walk of the graph to determine what the combination is. However, VPP power users might consider this option for a limited set of their use cases where performance is truly king.
collapse multiple levels of load-balancing into one. For example, if there were two levels of load-balancing each with two choices, this could equally be represented by one level with 4 choices.
In either case a disadvantage to collapsing the graph is that it removes the indirection objects that provide fast convergence (see section Fast Convergence). To collapse is then a trade-off between faster forwarding and fast convergence; VPP favours the latter.
Footnotes: