Introduction
This tutorial shows how to use VPP use iperf3 and TRex to get some basic performance numbers from a few basic configurations. Four examples are shown. In the first two examples, the iperf3 tool is used to generate traffic, and in the last two examples the Cisco’s TRex Realistic Traffic Generator is used. For comparison purposes, the first example shows packet forwarding using ordinary kernel IP forwarding, and the second example shows packet forwarding using VPP.
Three Intel Xeon processor platform systems are used to connect to the VPP host to pass traffic using iperf3 and Cisco’s TRex.
Intel 40 Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) network interface cards (NICs) are used to connect the hosts.
Using Kernel Packet Forwarding with Iperf3
In this test, 40 GbE Intel Ethernet Network Adapters are used to connect the three systems. Figure 1 illustrates this configuration.
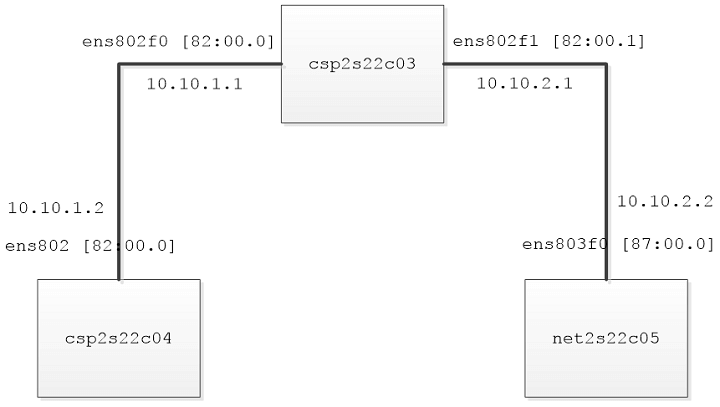
Figure 1: VPP runs on a host that connects to two other systems via 40 GbE NICs.
For comparison purposes, in the first example, we configure kernel forwarding in csp2s22c03 and use the iperf3 tool to measure network bandwidth between csp2s22c03 and net2s22c05.
In the second example, we start the VPP engine in csp2s22c03 instead of using kernel forwarding. On csp2s22c03, we configure the system to have the addresses 10.10.1.1/24 and 10.10.2.1/24 on the two 40-GbE NICs. To find all network interfaces available on the system, use the lshw Linux command to list all network interfaces and the corresponding slots [0000:xx:yy.z].
In this example, the 40-GbE interfaces are ens802f0 and ens802f1.
csp2s22c03$ sudo lshw -class network -businfo
Bus info Device Class Description
========================================================
pci@0000:03:00.0 enp3s0f0 network Ethernet Controller 10-Gig
pci@0000:03:00.1 enp3s0f1 network Ethernet Controller 10-Gig
pci@0000:82:00.0 ens802f0 network Ethernet Controller XL710
pci@0000:82:00.1 ens802f1 network Ethernet Controller XL710
pci@0000:82:00.0 ens802f0d1 network Ethernet interface
pci@0000:82:00.1 ens802f1d1 network Ethernet interface
Configure the system csp2s22c03 to have 10.10.1.1 and 10.10.2.1 on the two 40-GbE NICs ens802f0 and ens802f1, respectively.
csp2s22c03$ sudo ip addr add 10.10.1.1/24 dev ens802f0
csp2s22c03$ sudo ip link set dev ens802f0 up
csp2s22c03$ sudo ip addr add 10.10.2.1/24 dev ens802f1
csp2s22c03$ sudo ip link set dev ens802f1 up
List the route table:
csp2s22c03$ route
Kernel IP routing table
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
default jf111-ldr1a-530 0.0.0.0 UG 0 0 0 enp3s0f1
default 192.168.0.50 0.0.0.0 UG 100 0 0 enp3s0f0
10.10.1.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 ens802f0
10.10.2.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 ens802f1
10.23.3.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 0 0 0 enp3s0f1
link-local * 255.255.0.0 U 1000 0 0 enp3s0f1
192.168.0.0 * 255.255.255.0 U 100 0 0 enp3s0f0
csp2s22c03$ ip route
default via 10.23.3.1 dev enp3s0f1
default via 192.168.0.50 dev enp3s0f0 proto static metric 100
10.10.1.0/24 dev ens802f0 proto kernel scope link src 10.10.1.1
10.10.2.0/24 dev ens802f1 proto kernel scope link src 10.10.2.1
10.23.3.0/24 dev enp3s0f1 proto kernel scope link src 10.23.3.67
169.254.0.0/16 dev enp3s0f1 scope link metric 1000
192.168.0.0/24 dev enp3s0f0 proto kernel scope link src 192.168.0.142 metric 100
On csp2s22c04, we configure the system to have the address 10.10.1.2 and use the interface ens802 to route IP packets 10.10.2.0/24. Use the lshw Linux command to list all network interfaces and the corresponding slots [0000:xx:yy.z].
For example, the interface ens802d1 (ens802) is connected to slot [82:00.0]:
csp2s22c04$ sudo lshw -class network -businfo
Bus info Device Class Description
=====================================================
pci@0000:03:00.0 enp3s0f0 network Ethernet Controller 10-Gigabit X540-AT2
pci@0000:03:00.1 enp3s0f1 network Ethernet Controller 10-Gigabit X540-AT2
pci@0000:82:00.0 ens802d1 network Ethernet Controller XL710 for 40GbE QSFP+
pci@0000:82:00.0 ens802 network Ethernet interface
For kernel forwarding, set 10.10.1.2 to the interface ens802, and add a static route for IP packet 10.10.2.0/24:
csp2s22c04$ sudo ip addr add 10.10.1.2/24 dev ens802
csp2s22c04$ sudo ip link set dev ens802 up
csp2s22c04$ sudo ip route add 10.10.2.0/24 via 10.10.1.1
csp2s22c04$ ifconfig
enp3s0f0 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr a4:bf:01:00:92:73
inet addr:10.23.3.62 Bcast:10.23.3.255 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::a6bf:1ff:fe00:9273/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:3411 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:1179 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:262230 (262.2 KB) TX bytes:139975 (139.9 KB)
ens802 Link encap:Ethernet HWaddr 68:05:ca:2e:76:e0
inet addr:10.10.1.2 Bcast:0.0.0.0 Mask:255.255.255.0
inet6 addr: fe80::6a05:caff:fe2e:76e0/64 Scope:Link
UP BROADCAST RUNNING MULTICAST MTU:1500 Metric:1
RX packets:0 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:40 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1000
RX bytes:0 (0.0 B) TX bytes:5480 (5.4 KB)
lo Link encap:Local Loopback
inet addr:127.0.0.1 Mask:255.0.0.0
inet6 addr: ::1/128 Scope:Host
UP LOOPBACK RUNNING MTU:65536 Metric:1
RX packets:31320 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 frame:0
TX packets:31320 errors:0 dropped:0 overruns:0 carrier:0
collisions:0 txqueuelen:1
RX bytes:40301788 (40.3 MB) TX bytes:40301788 (40.3 MB)
After setting the route, we can ping from csp2s22c03 to csp2s22c04, and vice versa:
csp2s22c03$ ping 10.10.1.2 -c 3
PING 10.10.1.2 (10.10.1.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.10.1.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.122 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.1.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.109 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.1.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.120 ms
csp2s22c04$ ping 10.10.1.1 -c 3
PING 10.10.1.1 (10.10.1.1) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.10.1.1: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=0.158 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.1.1: icmp_seq=2 ttl=64 time=0.096 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.1.1: icmp_seq=3 ttl=64 time=0.102 ms
Similarly, on net2s22c05, we configure the system to have the address 10.10.2.2 and use the interface ens803f0 to route IP packets 10.10.1.0/24. Use the lshw Linux command to list all network interfaces and the corresponding slots [0000:xx:yy.z]. For example, the interface ens803f0 is connected to slot [87:00.0]:
NET2S22C05$ sudo lshw -class network -businfo
Bus info Device Class Description
========================================================
pci@0000:03:00.0 enp3s0f0 network Ethernet Controller 10-Gigabit X540-AT2
pci@0000:03:00.1 enp3s0f1 network Ethernet Controller 10-Gigabit X540-AT2
pci@0000:81:00.0 ens787f0 network 82599 10 Gigabit TN Network Connection
pci@0000:81:00.1 ens787f1 network 82599 10 Gigabit TN Network Connection
pci@0000:87:00.0 ens803f0 network Ethernet Controller XL710 for 40GbE QSFP+
pci@0000:87:00.1 ens803f1 network Ethernet Controller XL710 for 40GbE QSFP+
For kernel forwarding, set 10.10.2.2 to the interface ens803f0, and add a static route for IP packet 10.10.1.0/24:
NET2S22C05$ sudo ip addr add 10.10.2.2/24 dev ens803f0
NET2S22C05$ sudo ip link set dev ens803f0 up
NET2S22C05$ sudo ip route add 10.10.1.0/24 via 10.10.2.1
After setting the route, you can ping from csp2s22c03 to net2s22c05, and vice versa. However, in order to ping between net2s22c05 and csp2s22c04, kernel IP forwarding in csp2s22c03 has to be enabled:
csp2s22c03$ sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 0
csp2s22c03$ echo 1 | sudo tee /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
csp2s22c03$ sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
If successful, verify that now you can ping between net2s22c05 and csp2s22c04:
NET2S22C05$ ping 10.10.1.2 -c 3
PING 10.10.1.2 (10.10.1.2) 56(84) bytes of data.
64 bytes from 10.10.1.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=63 time=0.239 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.1.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=63 time=0.224 ms
64 bytes from 10.10.1.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=63 time=0.230 ms
We use the iperf3 utility to measure network bandwidth between hosts. In this test, we download the iperf3 utility tool on both net2s22c05 and csp2s22c04. On csp2s22c04, we start the iperf3 server with “iperf3 –s”, and then on net2s22c05, we start the iperf3 client to connect to the server:
NET2S22C05$ iperf3 -c 10.10.1.2
Connecting to host 10.10.1.2, port 5201
[ 4] local 10.10.2.2 port 54074 connected to 10.10.1.2 port 5201
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Retr Cwnd
[ 4] 0.00-1.00 sec 936 MBytes 7.85 Gbits/sec 2120 447 KBytes
[ 4] 1.00-2.00 sec 952 MBytes 7.99 Gbits/sec 1491 611 KBytes
[ 4] 2.00-3.00 sec 949 MBytes 7.96 Gbits/sec 2309 604 KBytes
[ 4] 3.00-4.00 sec 965 MBytes 8.10 Gbits/sec 1786 571 KBytes
[ 4] 4.00-5.00 sec 945 MBytes 7.93 Gbits/sec 1984 424 KBytes
[ 4] 5.00-6.00 sec 946 MBytes 7.94 Gbits/sec 1764 611 KBytes
[ 4] 6.00-7.00 sec 979 MBytes 8.21 Gbits/sec 1499 655 KBytes
[ 4] 7.00-8.00 sec 980 MBytes 8.22 Gbits/sec 1182 867 KBytes
[ 4] 8.00-9.00 sec 1008 MBytes 8.45 Gbits/sec 945 625 KBytes
[ 4] 9.00-10.00 sec 1015 MBytes 8.51 Gbits/sec 1394 611 KBytes
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bandwidth Retr
[ 4] 0.00-10.00 sec 9.45 GBytes 8.12 Gbits/sec 16474 sender
[ 4] 0.00-10.00 sec 9.44 GBytes 8.11 Gbits/sec receiver
iperf Done.